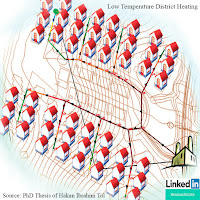
Network Types - Low Temperature District Heating

A short introduction about distribution network types with photos from nature. Please give a focus how the veins of these leafs in the photo are structured. Some branched, some having a loop formation and some a mixture of both! A question rises that highlights the necessity of distribution systems in our lives, especially district heating/cooling networks: why such natural elements have a structure of distribution instead of individual production? Please think about various forms of distribution in the nature: you can find lots of examples i.e. the blood vessels, neural system, etc.! The network layout (network topology) is briefly described after this inspiring-from-nature photo below. Network Types with Different Layouts as Observed in the Leafs: Inspiration to the Centralized Energy Networks Obvious that nature at most uses centralized distribution to satisfy the local needs. So do the district heating systems! Although in my publications the network layout was took...